ADHD: What is it, types, symptoms, prevalence, causes, diagnosis and treatment
What is ADHD?
ADHD is a brain-based disorder characterised by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with daily functioning. It’s not caused by laziness, poor discipline, or a lack of effort. Instead, ADHD stems from differences in brain development and function, particularly in areas responsible for executive functioning skills such as planning, organisation, and self-regulation. It impacts key areas of functioning, such as attention, impulse control, and emotional regulation, making daily life more challenging.
Although ADHD often begins in childhood, it can persist into adulthood, with many cases going undiagnosed until later in life. ADHD affects every individual differently, and its symptoms can change as people age. ADHD is characterised by two types of behavioural problems – inattention, and hyperactivity and impulsiveness. Most individuals with ADHD experience issues in both of these categories.
Get support for ADHD
Our team is available for a confidential conversation about what you are experiencing and how we can support you, through ADHD assessment and treatment. Complete the enquiry form below and our team will be in contact with you.
Types of ADHD
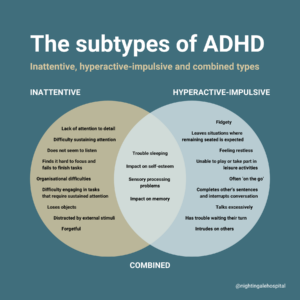
There are three subtypes of ADHD:
- Inattentive type
- Hyperactive-impulsive type
- Combined type
Inattentive type
People with inattentive ADHD (or ADHD-I) have difficulty sustaining attention, following detailed instructions, and organisation and tend to make careless mistakes without realising. They have problems with memory, can be easily distracted by external stimuli, and often lose things. The inattentive type of ADHD is more commonly diagnosed in adults and females than the hyperactive-impulsive type.
Hyperactive-impulsive type
People with hyperactive-impulsive ADHD (or ADHD-H) feel the need for constant movement – this may be fidgeting, squirming, and struggling to stay seated. People of all ages may talk almost constantly, interrupt others, blurt out answers, and struggle with self-control. The hyperactive-impulsive type of ADHD is more recognisable and more often diagnosed in children and men.
Combined type
The combined ADHD type (or ADHD-C) is the most common type of ADHD. People with the combined type have symptoms of both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive types.
Symptoms of ADHD in adults
Due to ADHD being a developmental disorder, it is widely believed that it cannot develop in adulthood without appearing at some point in someone’s childhood. Symptoms of ADHD usually start in childhood and are noticeable before the age of 6. However, in some cases, ADHD is not recognised until adulthood, when symptoms are much harder to define.
In adulthood, hyperactivity symptoms tend to decrease, whilst restlessness, impulsiveness and difficulty concentrating may continue.
Signs and symptoms of ADHD in adults generally include:
- Carelessness or a lack of attention to detail
- A tendency to work on many projects simultaneously, which are seldom completed
- Organisational difficulties and procrastination
- A sense of underachievement
- A tendency to blurt things out without thinking, or interrupting others in conversation
- Forgetfulness
- Extreme impatience
- Restlessness and anxiety
- Impulsivity, a risk-taking mentality or searching for high stimulation
- Mood swings and irritability
ADHD can be linked to a variety of other mental health problems, including personality disorders, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), addiction and interpersonal difficulties.

Our consultant psychiatrists and therapists specialise in ADHD
We have a team of 45 consultant psychiatrists and over 100 therapists who specialise in treating a range of mental health disorders, including ADHD.
Our team are here to understand what you are experiencing and match you with a suitable specialist who will be able to put together an individualised treatment plan for you. Complete the enquiry form below and our team will contact you for a confidential discussion.
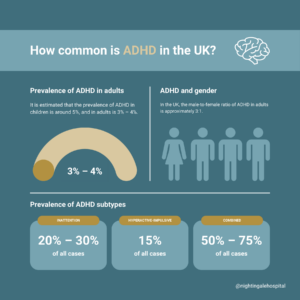
How common is ADHD in the UK?
- It is estimated that the prevalence of ADHD in children is around 5%, and in adults is 3% – 4%.1
- ADHD is more commonly diagnosed in males than females, with prevalence ratios in adults generally estimated at 3:1.1
- Each subtype of ADHD is diagnosed at different rates:1
- The inattentive subtype accounts for around 20% – 30% of cases.
- The hyperactive-impulsive subtype accounts for around 15% of cases.
- The combined subtype accounts for around 50% – 75% of cases.
References
What causes ADHD?
The causes of ADHD are not completely clear, therefore research into this area continues. Experts generally believe that ADHD can be a result of genetics, environment, and problems during early developmental years.
ADHD diagnosis
At Nightingale Hospital, our approach to the assessment and treatment of adult ADHD combines an individualised programme with treatments based on current clinical evidence.
The first step in accessing ADHD treatment is an ADHD assessment.
When should you consider an assessment?
If you or someone you know experiences persistent difficulties with focus, organisation, impulsivity, or restlessness that interfere with daily life, it may be time to consider an assessment. ADHD symptoms must be present in multiple settings (e.g., at work, school, and home) and persist for at least six months to meet diagnostic criteria.
Nightingale Hospital has many experts in the diagnosis and management of neurodevelopmental disorders in adults, including a range of consultant psychiatrists, clinical psychologists and therapists. You can find an appropriate specialist by using our specialist finder tool.
How Is ADHD diagnosed?
An ADHD assessment typically involves:
- Comprehensive Interviews: A clinician will ask about medical history, symptoms, and how they affect daily life.
- Standardised Questionnaires: Tools like the Conners, Vanderbilt scales, the DIVA or the Barkley Adult ADHD rating scales are often used to gather input from the individual and others (e.g., parents, teachers, or partners). Old school reports may be analysed and psychometric tests may be administered to support the diagnosis. The initial ADHD assessment takes approximately two hours followed by up to a few further hours of analysis and additional investigations if required. The assessment can be followed by a consultation with the psychiatrist to clarify the diagnosis of ADHD and offer ADHD treatment options.
- Rule-Out Conditions: Other medical or psychological conditions, like anxiety or learning disorders, are considered to ensure an accurate diagnosis
Treatment options for ADHD
While there’s no “cure” for ADHD, treatments can help manage symptoms effectively:
Medication:
- Stimulants are commonly prescribed and highly effective.
- Non-stimulants may be recommended for individuals who can’t tolerate stimulants.
Psychological and Occupational Therapy:
- Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) helps with organisation, emotional regulation, and negative thought patterns.
- Coaching and skills training focus on time management and productivity.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular exercise, healthy nutrition, and sleep routines support brain function.
- Tools like planners, apps, or reminders can improve organisation.
Support Systems:
- ADHD support groups offer a safe space for sharing experiences and strategies.
- Family or partner education can help improve relationships and understanding.
Are you a health professional?
If you’re looking to refer a patient, we have a team of 45 consultant psychiatrists and over 100 therapists who specialise in treating a range of mental health disorders, including ADHD. All referrals are carefully reviewed by our specialist multidisciplinary team to assess the suitability for the treatment programme.
The referral process for the ADHD day therapy programme begins with completing the Day Therapy Services Referral Form, which can be accessed by clicking below:
Enquire about
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Please contact us to find out more.
Enquire Now








